蜜獾算法(HBA)模拟了蜜獾的觅食行为。为了找到食物源,蜜獾要么嗅、挖,要么跟随蜜獾。第一种行为为挖掘模式,而第二种行为为采蜜模式。在挖掘模式中,它利用自己的嗅觉来确定猎物的大致位置;当到达那里时,它会绕着猎物移动,以选择合适的位置来挖掘和捕捉猎物。在采蜜模式中,蜜獾利用引导獾的位置直接定位蜂巢。
1 初始化阶段
初始化蜜獾的数量(种群规模)和个体的位置
2 定义强度I
强度和猎物的集中力以及和蜜獾之间的距离有关。I是猎物的气味强度;如果气味高,则运动速度快,反之亦然。
3 更新密度因子
密度因子α控制时变随机化,以确保从勘探到开采的平稳过渡。
4 跳出局部最优
5 更新个体位置
5.1 挖掘阶段
在挖掘阶段,蜜獾执行类似于心脏线形状的动作。
5.2 采蜜阶段
蜜獾跟随蜂蜜向导獾到达蜂巢的情况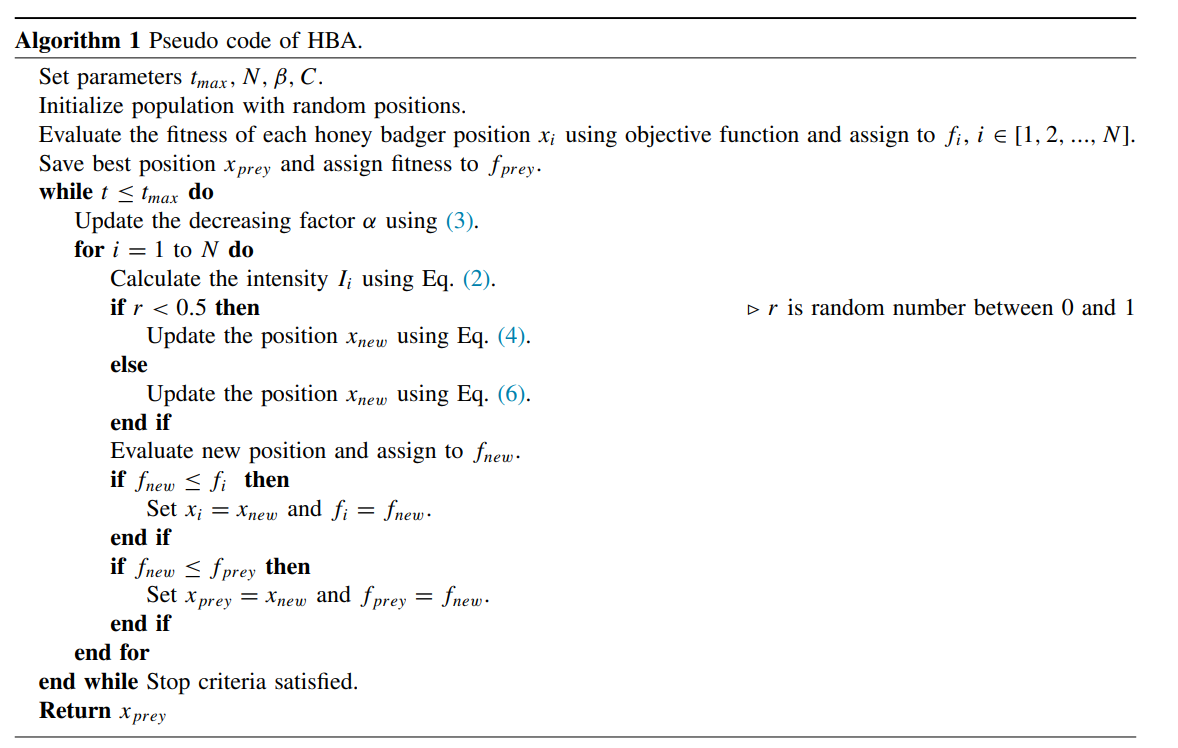

import random
import time
import numpy as np
rng = np.random.default_rng()
import math
import sys
from numpy import linalg as LA
def fun(X):
output = sum(np.square(X))
return output
# This function is to initialize the Honey Badger population.
def initial(pop, dim, ub, lb):
X = np.zeros([pop, dim])
for i in range(pop):
for j in range(dim):
X[i, j] = random.random() * (ub[j] - lb[j]) + lb[j]
return X
# Calculate fitness values for each Honey Badger.
def CaculateFitness1(X, fun):
fitness = fun(X)
return fitness
# Sort fitness.
def SortFitness(Fit):
fitness = np.sort(Fit, axis=0)
index = np.argsort(Fit, axis=0)
return fitness, index
# Sort the position of the Honey Badger according to fitness.
def SortPosition(X, index):
Xnew = np.zeros(X.shape)
for i in range(X.shape[0]):
Xnew[i, :] = X[index[i], :]
return Xnew
# Boundary detection function.
def BorderCheck1(X, lb, ub, dim):
for j in range(dim):
if X[j] < lb[j]:
X[j] = ub[j]
elif X[j] > ub[j]:
X[j] = lb[j]
return X
def Intensity(pop, GbestPositon, X):
epsilon = 0.00000000000000022204
di = np.zeros(pop)
S = np.zeros(pop)
I = np.zeros(pop)
for j in range(pop):
if (j <= pop):
di[j] = LA.norm([[X[j, :] - GbestPositon + epsilon]])
S[j] = LA.norm([X[j, :] - X[j + 1, :] + epsilon])
di[j] = np.power(di[j], 2)
S[j] = np.power(S[j], 2)
else:
di[j] = [LA.norm[[X[pop, :] - GbestPositon + epsilon]]]
S[j] = [LA.norm[[X[pop, :] - X[1, :] + epsilon]]]
di[j] = np.power(di[j], 2)
S[j] = np.power(S[j], 2)
for i in range(pop):
n = random.random()
I[i] = n * S[i] / [4 * math.pi * di[i]*di[i]]
return I
def hba(pop, dim, lb, ub, Max_iter, fun):
X = initial(pop, dim, lb, ub) # Initialize the number of honey badgers
fitness = np.zeros([pop, 1])
for i in range(pop):
fitness[i] = CaculateFitness1(X[i, :], fun)
fitness, sortIndex = SortFitness(fitness) # Sort the fitness values of honey badger.
X = SortPosition(X, sortIndex) # Sort the honey badger.
GbestScore = fitness[0] # The optimal value for the current iteration.
GbestPositon = np.zeros([1, dim])
GbestPositon[0, :] = X[0, :]
Curve = np.zeros([Max_iter, 1])
C = 2 # constant in Eq. (3)
beta = 6 # the ability of HB to get the food Eq.(4)
vec_flag = [1, -1]
vec_flag = np.array(vec_flag)
Xnew = np.zeros([pop, dim])
for t in range(Max_iter):
# print("iteration: ",t)
alpha = C * math.exp(-t / Max_iter); # density factor in Eq. (3)
I = Intensity(pop, GbestPositon, X); # intensity in Eq. (2)
Vs = random.random()
for i in range(pop):
Vs = random.random()
F = vec_flag[math.floor((2 * random.random()))]
for j in range(dim):
di = GbestPositon[0, j] - X[i, j]
if (Vs < 0.5): # Digging phase Eq. (4)
r3 = np.random.random()
r4 = np.random.randn()
r5 = np.random.randn()
Xnew[i, j] = GbestPositon[0, j] + F * beta * I[i] * GbestPositon[0, j] + F * r3 * alpha * (
di) * np.abs(math.cos(2 * math.pi * r4) * (1 - math.cos(2 * math.pi * r5)));
else:
r7 = random.random()
Xnew[i, j] = GbestPositon[0, j] + F * r7 * alpha * di; # Honey phase Eq. (6)
# print(di)
Xnew[i, :] = BorderCheck1(Xnew[i, :], lb, ub, dim)
tempFitness = CaculateFitness1(Xnew[i, :], fun)
if (tempFitness <= fitness[i]):
fitness[i] = tempFitness
X[i, :] = Xnew[i, :]
for i in range(pop):
X[i, :] = BorderCheck1(X[i, :], lb, ub, dim)
Ybest, index = SortFitness(fitness) # Sort fitness values.
if (Ybest[0] <= GbestScore):
GbestScore = Ybest[0] # Update the global optimal solution.
GbestPositon[0, :] = X[index[0], :] # Sort fitness values
Curve[t] = GbestScore
return GbestScore, GbestPositon, Curve
rng = np.random.default_rng()
time_start = time.time()
pop = 50 # Honey Badger population size.
MaxIter = 300 # Maximum number of iterations.
dim = 20 # The dimension.
fl = -10 # The lower bound of the search interval.
ul = 10 # The upper bound of the search interval.
lb = fl * np.ones([dim, 1])
ub = ul * np.ones([dim, 1])
GbestScore, GbestPositon, Curve = hba(pop, dim, lb, ub, MaxIter, fun)
time_end = time.time()
print(f"The running time is: {time_end - time_start} s")
print('The optimal value:', GbestScore)
print('The optimal solution:', GbestPositon)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(Curve, color='dodgerblue', marker='o', markeredgecolor='k', markerfacecolor='dodgerblue')
ax.set_xlabel('Number of Iterations', fontsize=15)
ax.set_ylabel('Fitness', fontsize=15)
ax.set_title('Honey Badger Optimization')
plt.show()